In order to dig dinosaurs, you must first really dig dinosaurs. That is, like them a lot, because the physical digging/excavating/collecting of dinosaurs is not for the faint-hearted. It’s a grueling, exhausting, painful exercise in self-denial – until such time as the precious fossils are finally secured in the museum collection or exhibit hall.
[READ MORE]The Official City of Cincinnati Fossil
The Cincinnati Dry Dredgers – a group of amateur paleontologists and geologists that have collected fossils and studied paleontology in the region for over 80 years – chose five candidates for the official Cincinnati fossil.
[READ MORE]Cincinnati’s Vanished Yellow Wares
Their yellow colors were bright and cheerful, a sharp contrast to their dull sanitary and kitchenware predecessors – redwares and stonewares. Nineteenth-century American yellow wares, earthenwares with a buff paste and a clear glaze, were both functional and inexpensive. In most cases, they were the product of an assembly line process – a system that attempted to standardize output using relatively cheap raw materials and labor.
[READ MORE]CMC’s COVID-19 Collecting Initiative
Early in the pandemic, we encouraged people to document how their lives had changed due to COVID-19. We weren’t sure what we would get but we all agreed we should put out an invitation to the community to share and record these unusual times.
[READ MORE]Where the “Buffalo” Roam(ed)
In September 2008, CMC excavated modern bison bones (Bison bison) that had recently been discovered in the channel of Big Bone Creek, the shallow stream that traverses the valley containing the lick. Remains of at least five sub-adult animals were collected, as were a dozen Native American stone artifacts found in close association with the bones. The artifacts were identified as expedient butchering tools that had been manufactured on-site from local materials and discarded after use.
[READ MORE]Prehistoric Bison
Two prehistoric bison species became known to science when their fossils were discovered in Boone County, Kentucky, home of the Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport and just down I-71/75 from Cincinnati. The Giant Bison, Bison latifrons, was identified from a skull fragment found around 1800 in the bed of a stream, likely either Gunpowder or Woolper Creek.
[READ MORE]Seeing Beneath the Ground: Remote Sensing at the Hahn Site
You may wonder how Cincinnati Museum Center’s archaeologists decide where to dig when we excavate a site. In part, our decisions are based on which questions we are trying to answer (e.g. what did they eat, how did they cook, what were their houses like, etc.), and on how much we can accomplish within a short amount of time. But, to answer most of these questions, it is helpful to know with some accuracy what lies beneath the surface. For this, we turn to ground-based remote sensing, also known as archaeological geophysics.
[READ MORE]Maya Mammals (and more!)
If you visit Maya: The Exhibition, one thing you will notice is how often animals are represented in the artifacts shown, and even in the glyphs used in their ancient writing system. Historic and modern cultures all around the world often use images of animals in their art and to decorate everyday objects. These animals might be important food sources, or religious or cultural symbols, or even pets.
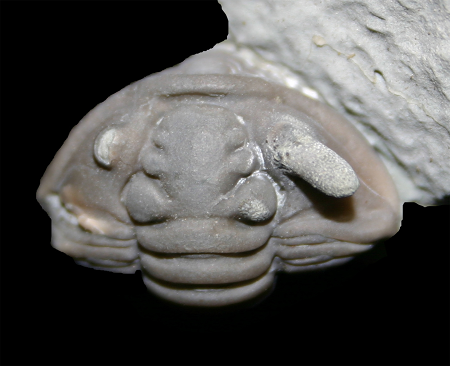
[READ MORE]Encrustation! Species Interaction in the Fossil Record
Encrusted fossil specimens are important because they provide direct evidence of species interaction at a single point in geological time. With this information, paleontologists can reconstruct community composition, the ecological roles of various fossil organisms and the biological implications of such interactions.
[READ MORE]That can’t be good! (for a fossil)
Why then would anyone want to damage a fossil bone by removing a section of it with a power drill? Surely this must be a wanton act of vandalism! Read our latest blog entry to learn why museums sometimes have to break a few eggs to make an omelet and drill a few bones to make a discovery.
[READ MORE]